Primary Prevention
Healthy habits not only reduce your risk for cancer but also lower the risk of developing other diseases. They also increase your general well-being and improve your physical appearance. What we eat, lack of physical activity, sun exposure, environmental pollution, alcohol and especially smoking are the main risk factors rather than genetic predisposition. Understanding these factors allows us to act positively, at least in some cases, and to lower the risk of developing cancer.
- Smoking causes 30% of all cancer deaths.
- Ninety percent of people with lung cancer are smokers.
- Being overweight and poor diet are linked to 40% of cancer-related deaths.
- Between 50% and 70% of skin cancers are linked to sun exposure. Mortality from alcohol-related cancer accounts for 3.5%.

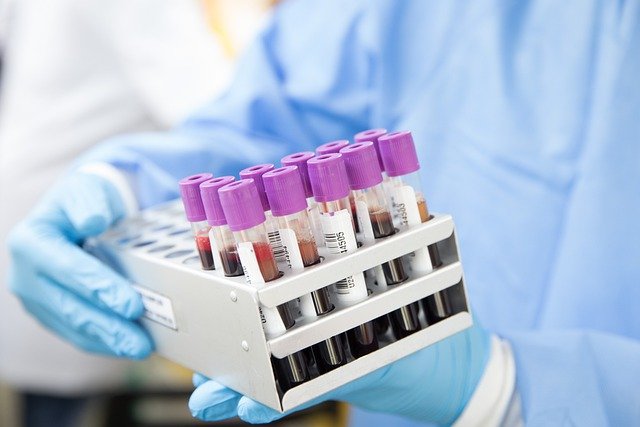
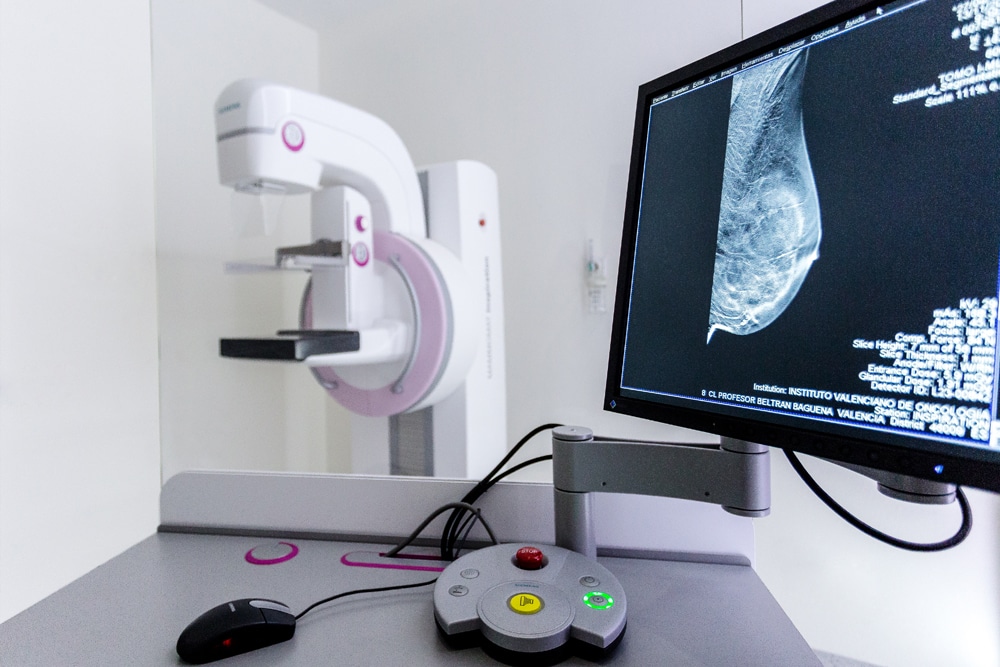
Secondary Prevention
The main goal of secondary prevention is to gain an advantage in the race to defeat cancer, to detect tumours before they become malignant or are in initial stages of the disease.
A small percentage of cancers (between 5% and 10%) in Spain are hereditary. Genetic counselling is a process that assesses the chance of disease when an individual has a personal or family history suggestive of genetic cancer susceptibility. Nevertheless, not every person that presents this predisposition will develop cancer sometime during their life. However, the cure rate is between 70% and 90% if cancer is confined and diagnosed in time,
Hence the importance of participating in secondary prevention programs (early detection and genetic counselling), particularly for patients who are at risk either because of age or sex. It provides an invaluable help to detect cancer in time.
In this way, the incidence rate of certain types of cancer could be reduced by:
- Breast cancer, 90%
- Colon cancer, 90%
- Skin cancer, 100%
- Lung cancer, 80% if detected in first stage
- Cervical cancer, 80%